5.4- switch- case -default語(yǔ)句


| 類型 | 描述 | bit | 最小值 | 最大值 |
| byte |
8位整數(shù)
|
8 | -128 (-2^7) | 127 (2^7-1) |
| short |
16位整數(shù)
|
16 | -32,768 (-2^15) | 32,767 (2^15 -1) |
| int |
32位整數(shù)
|
32 |
- 2,147,483,648 (-2^31) |
2,147,483,647 (2^31 -1) |
| long |
64位整數(shù)
|
64 |
-9,223,372,036,854,775,808 (-2^63) |
9,223,372,036,854,775,807 (2^63 -1) |
| float |
32位實(shí)數(shù)
|
32 | -3.4028235 x 10^38 | 3.4028235 x 10^38 |
| double |
64位實(shí)數(shù)
|
64 | -1.7976931348623157 x 10^308 | 1.7976931348623157 x 10^308 |
| boolean |
邏輯類型
|
|
false | true |
| char |
字符
|
16 | '\u0000' (0) | '\uffff' (65,535). |
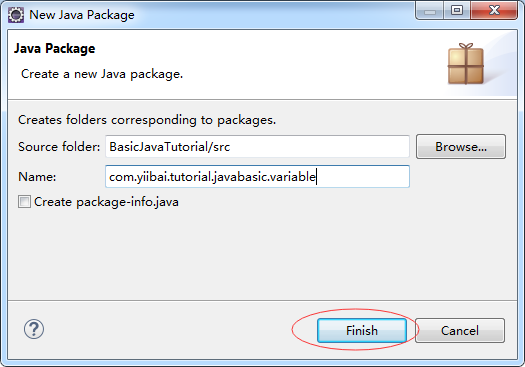

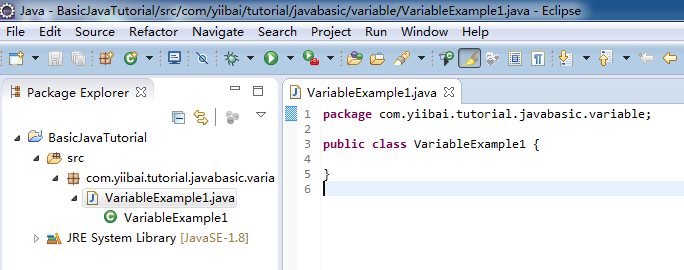
package com.yiibai.tutorial.javabasic.variable;
public class VariableExample1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Declare a variable of type int (integer 32-bit)
int firstNumber;
// Assigning values to firstNumber
firstNumber = 10;
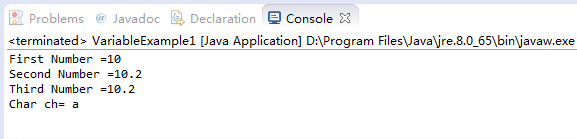
System.out.println("First Number =" + firstNumber);
// Declare a 32-bit real number (float)
// This number is assigned a value of 10.2
float secondNumber = 10.2f;
System.out.println("Second Number =" + secondNumber);
// Declare a 64-bit real numbers
// This number is assigned a value of 10.2
// character d at the end to tell with Java this is the type double.
// Distinguished from a float.
double thirdNumber = 10.2d;
System.out.println("Third Number =" + thirdNumber);
// Declare a character
char ch = 'a';
System.out.println("Char ch= " + ch);
}
}
package com.yiibai.tutorial.javabasic.variable;
public class VariableExample2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Declare three 64-bit integer (long)
long firstNumber, secondNumber, thirdNumber;
// Assign value to firstNumber
// L at the end to tell java a long type, distinguished from type int.
firstNumber = 100L;
// Assign values to secondNumber
secondNumber = 200L;
// Assign values to thirdNumber
thirdNumber = firstNumber + secondNumber;
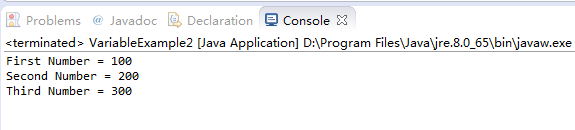
System.out.println("First Number = " + firstNumber);
System.out.println("Second Number = " + secondNumber);
System.out.println("Third Number = " + thirdNumber);
}
}
if(condition1 true) {
// Do something here
}elseif(condition2 true) {
// Do something here
}elseif(condition3 true) {
// Do something here
}else { // Other
// Do something here
}
package com.yiibai.tutorial.javabasic.controlflow;
public class ElseIfExample1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Declaring a integer number (int)
int score = 20;
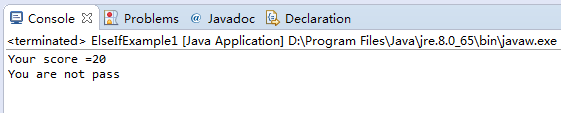
System.out.println("Your score =" + score);
// If the score is less than 50
if (score < 50) {
System.out.println("You are not pass");
}
// Else if the score more than or equal to 50 and less than 80.
else if (score >= 50 && score < 80) {
System.out.println("You are pass");
}
// Remaining cases (that is greater than or equal to 80)
else {
System.out.println("You are pass, good student!");
}
}
}
int score = 80;
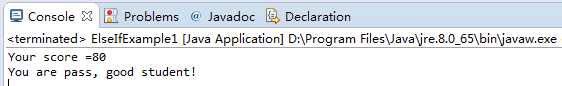
package com.yiibai.tutorial.javabasic.controlflow;
public class ElseIfExample2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Declare a variable int simulate your age.
int age = 20;
// Test age less than or equal 17
if (age <= 17) {
System.out.println("You are 17 or younger");
}
// Test age equals 18
else if (age == 18) {
System.out.println("You are 18 year old");
}
// Test age, greater than 18 and less than 40
else if (age > 18 && age < 40) {
System.out.println("You are between 19 and 39");
}
// Remaining cases (Greater than or equal to 40)
else {
// Nested if statements
// Test age not equals 50.
if (age != 50) {
System.out.println("You are not 50 year old");
}
// Negative statements
if (!(age == 50)) {
System.out.println("You are not 50 year old");
}
// If age is 60 or 70
if (age == 60 || age == 70) {
System.out.println("You are 60 or 70 year old");
}
}
}
}
package com.yiibai.tutorial.javabasic.controlflow;
public class BooleanExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Declare a variable of type boolean
boolean value = true;
// If value is true
if (value == true) {
System.out.println("It's true");
}
// Else
else {
System.out.println("It's false");
}
// With boolean values you can also write
if (value) {
System.out.println("It's true");
}
// Else
else {
System.out.println("It's false");
}
}
}
switch( variable_to_test ) {
casevalue:
// code_here;
break;
casevalue:
// code_here;
break;
default:
// values_not_caught_above;
}
package com.yiibai.tutorial.javabasic.controlflow;
public class SwitchExample1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Declare a variable age
int age = 20;
// Check the value of age
switch (age) {
// Case age = 18
case 18:
System.out.println("You are 18 year old");
break;
// Case age = 20
case 20:
System.out.println("You are 20 year old");
break;
// Remaining cases
default:
System.out.println("You are not 18 or 20 year old");
}
}
}
You are 20 year old
// This is not allowed !! case(age < 18) : // case only accept a specific value eg: case18: // Do something here break;
package com.yiibai.tutorial.javabasic.controlflow;
public class SwitchExample2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Declare a variable age
int age = 30;
// Check the value of age
switch (age) {
// Case age = 18
case 18:
System.out.println("You are 18 year old");
// Case age in 20, 30, 40
case 20:
case 30:
case 40:
System.out.println("You are " + age);
break;
// Remaining case:
default:
System.out.println("Other age");
}
}
}
You are 30
for( start_value; end_value; increment_number ) {
// Code here
}
packagecom.yiibai.tutorial.javabasic.loop;
publicclass ForLoopExample1 {
publicstaticvoidmain(String[] args) {
// Declare a variable, step in loop
intstep = 1;
// Declare a variable value with the start value is 0
// After each iteration, value will increase 3
// And the loop will end when the value greater than or equal to 10
for(intvalue = 0; value < 10; value = value + 3) {
System.out.println("Step ="+ step + " value = "+ value);
// Increase 1
step = step + 1;
}
}
}
Step =1 value = 0 Step =2 value = 3 Step =3 value = 6 Step =4 value = 9
package com.yiibai.tutorial.javabasic.loop;
public class ForLoopExample2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int sum = 0; for (int i = 0; i <= 100; i = i + 1) {
sum = sum + i;
}
System.out.println(sum); }
}
5050
// While the condition is true, then do something.
while( 條件為真 ) {
// Do something here.
}
參見圖示
publicclassWhileExampe1 {
publicstaticvoidmain(String[] args) {
intvalue = 3;
// While the value is less than 10, the loop is working.
while( value < 10) {
System.out.println("Value = "+ value);
// Increase value by adding 2
value = value + 2;
}
}
}
// The do-while loop to work at least one round
// and while the condition is true, it also works to
do{
// Do something here.
}while( condition );
package com.yiibai.tutorial.javabasic.loop;
public class DoWhileExample1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int value = 3;
// do-while loop will execute at least once
do {
System.out.println("Value = " + value);
// Increase 3
value = value + 3;
} while (value < 10);
}
}
Value = 3 Value = 6 Value = 9
// Declare an array, not a specified number of elements.
int[] array1;
// Initialize the array with 100 elements
// The element has not been assigned a specific value
array1 = newint[100];
// Declare an array specifies the number of elements
// The element has not been assigned a specific value
double[] array2 = newdouble[10];
// Declare an array whose elements are assigned specific values.
// This array with 4 elements
long[] array3= {10L, 23L, 30L, 11L};
package com.yiibai.tutorial.javabasic.array;
public class ArrayExample1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Declare an array with 5 elements
int[] myArray = new int[5];
// Note: the first element of the array index is 0:
// Assigning values to the first element (index 0)
myArray[0] = 10;
// Assigning values to the second element (index 1)
myArray[1] = 14;
myArray[2] = 36;
myArray[3] = 27;
// Value for the 5th element (the last element in the array)
myArray[4] = 18;
// Print out element count.
System.out.println("Array Length=" + myArray.length);
// Print to Console element at index 3 (4th element in the array)
System.out.println("myArray[3]=" + myArray[3]);
// Use a for loop to print out the elements in the array.
for (int index = 0; index < myArray.length; index++) {
System.out.println("Element " + index + " = " + myArray[index]);
}
}
}
Array Length=5 myArray[3]=27 Element 0 = 10 Element 1 = 14 Element 2 = 36 Element 3 = 27 Element 4 = 18
package com.yiibai.tutorial.javabasic.array;
public class ArrayExample2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Declare an array with 5 elements
int[] myArray = new int[5];
// Print out element count
System.out.println("Array Length=" + myArray.length);
// Using loop assign values to elements of the array.
for (int index = 0; index < myArray.length; index++) {
myArray[index] = 100 * index * index + 3;
}
// Print out the element at index 3
System.out.println("myArray[3] = "+ myArray[3]);
}
}
Array Length=5 myArray[3] = 903
package com.yiibai.tutorial.javabasic.javastructure;
public class Person {
// This is field
// The name of Person
public String name;
// This is a Constructor
// Use it to initialize the object (Create new object)
// This constructor has one parameter
// Constructor always have the same name as the class.
public Person(String persionName) {
// Assign the value of the parameter into the 'name' field
this.name = persionName;
}
// This method returns a String ..
public String getName() {
return this.name;
}
}
package com.yiibai.tutorial.javabasic.javastructure;
public class PersonTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create an object of class Person
// Initialize this object via constructor of class Person
// Specifically, Edison
Person edison = new Person("Edison");
// Class Person has the method getName()
// Use the object to call getName():
String name = edison.getName();
System.out.println("Person 1: " + name);
// Create an object of class Person
// Initialize this object via constructor of class Person
// Specifically, Bill Gates
Person billGate = new Person("Bill Gates");
// Class Person has field name (public)
// Use objects to refer to it.
String name2 = billGate.name;
System.out.println("Person 2: " + name2);
}
}
Person 1: Edison Person 2: Bill Gates
package com.yiibai.tutorial.javabasic.javastructure;
public class FieldSample {
// This is static field.
public static int MY_STATIC_FIELD = 100;
// This is normal field.
public String myValue;
// Constructor
public FieldSample(String myValue) {
this.myValue= myValue;
}
}
package com.yiibai.tutorial.javabasic.javastructure;
public class FieldSampleTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create the first object.
FieldSample obj1 = new FieldSample("Value1");
System.out.println("obj1.myValue= " + obj1.myValue);
// Print out static value, access via instance of class (an object).
System.out.println("obj1.MY_STATIC_FIELD= " + obj1.MY_STATIC_FIELD);
// Print out static value, access via class.
System.out.println("FieldSample.MY_STATIC_FIELD= "
+ FieldSample.MY_STATIC_FIELD);
// Create second object:
FieldSample obj2 = new FieldSample("Value2");
System.out.println("obj2.myValue= " + obj2.myValue);
// Print out static value, access via instance of class (an object)
System.out.println("obj2.MY_STATIC_FIELD= " + obj2.MY_STATIC_FIELD);
System.out.println(" ------------- ");
// Set new value for static field.
// (Or using: FieldSample.MY_STATIC_FIELD = 200)
obj1.MY_STATIC_FIELD = 200;
// It will print out the value 200.
System.out.println("obj2.MY_STATIC_FIELD= " + obj2.MY_STATIC_FIELD);
}
}
obj1.myValue= Value1 obj1.MY_STATIC_FIELD= 100 FieldSample.MY_STATIC_FIELD= 100 obj2.myValue= Value2 obj2.MY_STATIC_FIELD= 100 ------------- obj2.MY_STATIC_FIELD= 200
package com.yiibai.tutorial.javabasic.javastructure;
public class FinalFieldExample {
// A final field.
// Final Field does not allow to assign new values.
public final int myValue = 100;
// A static final field.
// Final field does not allow to assign new values.
public static final long MY_LONG_VALUE = 1234L;
}
package com.yiibai.tutorial.javabasic.javastructure;
public class MethodSample {
public String text = "Some text";
// Default Constructor
public MethodSample() {
}
// This method return a String
// and has no parameter.
public String getText() {
return this.text;
}
// This is a method with one parameter String.
// This method returns void (not return anything)
public void setText(String text) {
// this.text reference to the text field.
// Distinguish the text parameter.
this.text = text;
}
// Static method
public static int sum(int a, int b, int c) {
int d = a + b + c;
return d;
}
}
package com.yiibai.tutorial.javabasic.javastructure;
public class MethodSampleTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create instance of MethodSample
MethodSample obj = new MethodSample();
// Call getText() method
String text = obj.getText();
System.out.println("Text = " + text);
// Call method setText(String)
obj.setText("New Text");
System.out.println("Text = " + obj.getText());
// Static method can be called through the class.
// This way is recommended. (**)
int sum = MethodSample.sum(10, 20, 30);
System.out.println("Sum 10,20,30= " + sum);
// Or call through objects
// This way is not recommended. (**)
int sum2 = obj.sum(20, 30, 40);
System.out.println("Sum 20,30,40= " + sum2);
}
}
Text = Some text Text = New Text Sum 10,20,30= 60 Sum 20,30,40= 90
package com.yiibai.tutorial.javabasic.inheritance;
public class Animal {
public Animal() {
}
public void move() {
System.out.println("Move ...!");
}
public void say() {
System.out.println("<nothing>");
}
}
package com.yiibai.tutorial.javabasic.inheritance;
public class Cat extends Animal {
// Override method o